The Post-9/11 GI Bill provides significant education benefits, including tuition and fee coverage, a monthly housing allowance, and a books and supplies stipend, to help eligible veterans and their families pursue higher education or training programs. It covers various approved institutions, from public universities to vocational schools.
GI Bill education benefits can be used for a wide range of approved programs, including degree and certificate programs, at the postsecondary level education such as colleges, universities, vocational, and technical schools. The Department of Veterans Affairs oversees the approval of these programs and institutions.
Eligibility generally requires a period of active service, with specific criteria varying by program. Basic eligibility is determined by the Department of Veterans Affairs and is generally based on service in the armed forces, including active duty and reserve military members. The “Forever GI Bill” has eliminated time limits for many, ensuring these crucial resources support veterans in achieving academic and career success, ultimately improving their long-term economic outlook.
Why This Update
VA education benefits are important to many veterans and their families. We want to make sure we have the best information possible to share with you!
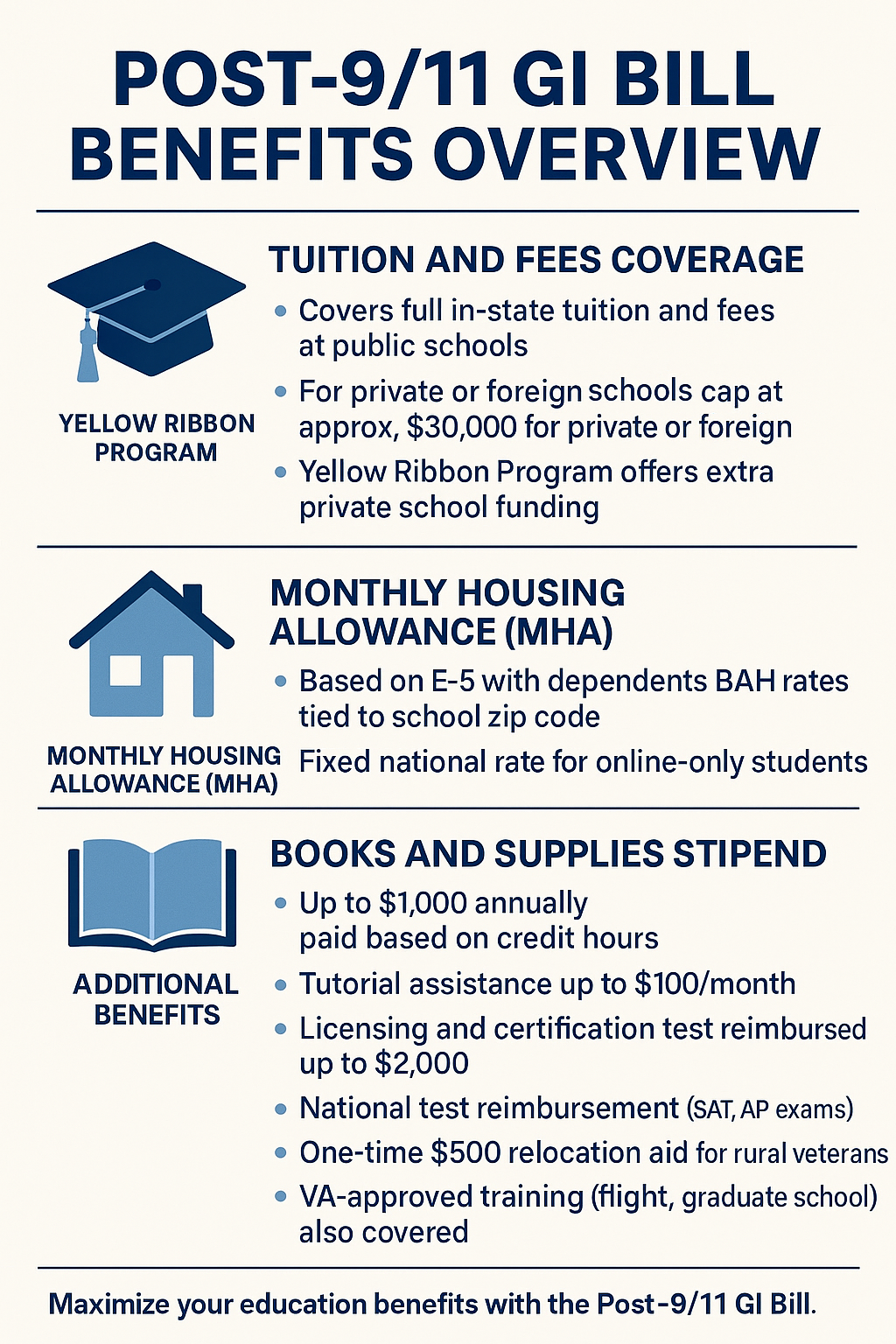
What GI Bill Education Benefits Cover
The Post-9/11 GI Bill covers full in-state tuition and fees at public institutions, with a national cap for private or foreign schools. For higher out-of-state, private, or graduate school tuition not fully covered by the GI Bill, the Yellow Ribbon Program helps students pay the remaining costs. This provision of the Yellow Ribbon Program only applies to those service members entitled to the maximum benefit rate. This may help veterans access quality education without the weight of tuition costs at state schools.
Beyond tuition, the program provides a Monthly Housing Allowance (MHA) based on the Basic Allowance for Housing (BAH) for an E-5 with dependents in your school’s zip code. This may help cover living expenses while you focus on your studies. Veterans also receive an annual stipend of up to $1,000 for books and supplies, prorated by eligibility percentage and paid directly to the student.
To receive payments, your school or training program must certify your enrollment.
To access education benefits, you need to submit an Application for VA Benefits (VA Form 22-1990), which can be done online or by submitting a paper application to the VA.
Who Qualifies for GI Bill Benefits?
Eligibility for the Post-9/11 GI Bill typically requires a minimum of 90 aggregate days of active duty service after September 10, 2001, with an honorable discharge.
The amount of benefits you receive depends on your length of service, with 36 months of qualifying service usually granting 100% of the Post-9/11 GI Bill benefits.
Some veterans may automatically qualify for 100% benefits regardless of service length. Purple Heart recipients may receive 100% benefits regardless of service length. Similarly, discharge due to a service-connected disability after 30 continuous days of service may also qualify for 100% benefits.
Different GI Bill programs have varying requirements. Specific service requirements apply for other programs like the Montgomery GI Bill Active Duty (MGIB-AD) and Montgomery GI Bill Selected Reserve (MGIB-SR). The MGIB-SR is available to members of the Army National Guard, Air National Guard, Army Reserve, Navy Reserve, Marine Corps Reserve, and other national guard armed forces, but not the Coast Guard Reserve.
To access the MGIB-SR benefit, eligible members must obtain a Notice of Basic Eligibility (DD Form 2384-1) from their unit. Additional education benefit programs and educational assistance programs include the GI Bill Selected Reserve, Reserve Educational Assistance Program (REAP), and Veterans Educational Assistance Program (VEAP), which provide training benefits to eligible veterans and reservists.
Extending Benefits to Family Members
One of the most valuable features of the Post-9/11 GI Bill is the ability to share your benefits with immediate family members, including spouses and children. Service members can transfer unused Post-9/11 GI Bill benefits to eligible spouses or children, provided the transfer is requested and approved while the member is serving in the Armed Forces.
To receive transferred educational benefits, a family member must be enrolled in the Defense Eligibility Enrollment Reporting System (DEERS). This may allow your educational investment to benefit your entire family.
The option to transfer benefits is open to any member of the armed forces who is eligible for the Post-9/11 GI Bill and has completed at least six years of service, and generally requires an additional 4-year service commitment at the time of transfer.
Children must typically be under 26, but cannot use the benefit until they receive a secondary school diploma or reach 18 years of age; a child’s subsequent marriage will not affect their eligibility. Spouses can often use benefits immediately. Upon approval, family members may apply to use transferred benefits with VA by submitting VA Form 22-1990e after the Department of Defense has approved the request for transfer. This flexibility may help families plan for educational expenses and career development.
For families who have experienced the ultimate sacrifice, additional programs provide support. The Fry Scholarship offers benefits similar to the Post-9/11 GI Bill for children and spouses of service members who died in the line of duty on or after September 11, 2001. The Survivors’ and Dependents’ Educational Assistance (DEA) Program (Chapter 35) offers aid to eligible dependents of veterans with permanent and total service-connected disabilities or those who died on active duty or from a service-connected disability.
Maximizing Your Education Benefits and Overcoming Challenges
Getting the most from your GI Bill education benefits requires careful planning and research. Research and choose accredited institutions with strong graduation rates, veteran support services, and positive employment outcomes. The quality of your educational institution may impact your career prospects and return on investment. You can receive benefits until your eligibility period ends or you use all of your entitlement, whichever comes first.
Service members must verify their enrollment at the end of each month to continue receiving Montgomery GI Bill payments. The VA can restore benefits in cases where education is disrupted due to school closure or other administrative issues.
Consult VA education counselors and veteran service organizations (VSOs) for personalized guidance and information. These resources may help you navigate the system and avoid common pitfalls.

Impact and Alternative Educational Pathways
The potential impact of GI Bill education benefits may extend far beyond the classroom. These benefits represent important tools for veterans working toward successful civilian careers. The Department of Veterans Affairs continues to offer several GI Bill programs as of 2026, and the GI Bill and related college fund programs have helped qualifying veterans and their families pay for education and training costs.
The “Forever GI Bill” eliminated time limits for Post-9/11 GI Bill benefits for veterans discharged on or after January 1, 2013. This may reduce pressure to rush through education and may allow veterans to pursue their academic goals on a timeline that works for their lives. Veterans discharged before this date may still have a 15-year expiration period from their last discharge.
Alternative programs include the Montgomery GI Bill (Active Duty and Selected Reserve) for different service qualifications. These benefits are generally payable for 10 years following a service member’s release from active duty. The Montgomery GI Bill requires a financial commitment from the service member, who must forfeit $100 per month for 12 months to qualify, and if the benefits are not used, the service member cannot recoup the money paid into the system. Military pay can also be used to fund educational benefits through certain programs.
Specialized programs like Veterans Readiness and Employment (VR&E) (Chapter 31) and VET TEC offer targeted support for veterans with service-connected disabilities or for high-tech training.
Example Scenario
After serving six years in the Army, David decided to pursue a Bachelor’s degree in Civil Engineering. He used his Post-9/11 GI Bill to cover 100% of his in-state tuition at a public university and received a monthly housing allowance, which allowed him to focus on his studies. The additional books and supplies stipend helped him purchase expensive textbooks, supporting his path to graduation and employment in an engineering role.
Frequently Asked Questions
What exactly does the Post-9/11 GI Bill cover?
The Post-9/11 GI Bill covers full in-state tuition and fees at public schools, a national cap for private institutions, a monthly housing allowance (MHA), and an annual stipend for books and supplies. It also provides funds for tutorial assistance and reimbursement for certain licensing and certification tests.
How many months of service do I need for 100% GI Bill benefits?
Generally, 36 months of aggregate active duty service after September 10, 2001, is required to qualify for 100% of the Post-9/11 GI Bill benefits. Purple Heart recipients and those discharged for a service-connected disability after 30 continuous days also receive 100%.
Can my spouse or children use my GI Bill benefits?
Yes, eligible service members can transfer unused Post-9/11 GI Bill benefits to a spouse or children. This typically requires 6 years of service and an additional 4-year service commitment, with specific age and enrollment requirements for dependents.
Is there a time limit for using my GI Bill benefits?
For veterans whose last discharge date was on or after January 1, 2013, the ‘Forever GI Bill’ eliminated the time limit for using Post-9/11 GI Bill benefits. Veterans discharged before this date may still have a 15-year expiration period from their last discharge.
What is the Yellow Ribbon Program and how does it work?
The Yellow Ribbon Program helps cover tuition and fees that exceed the Post-9/11 GI Bill’s maximum benefit for private or foreign schools. Participating institutions voluntarily enter into an agreement with the VA to fund a portion of the unmet costs, which the VA then matches.
What are some alternative education benefits if I don’t qualify for the Post-9/11 GI Bill?
Alternative programs include the Montgomery GI Bill (Active Duty – Chapter 30, and Selected Reserve – Chapter 1606), the Survivors’ and Dependents’ Educational Assistance (DEA – Chapter 35) Program, and Veterans Readiness and Employment (VR&E – Chapter 31) for those with service-connected disabilities.
How do GI Bill benefits affect a veteran’s career and earnings long-term?
Research indicates that veterans who utilize their GI Bill benefits experience higher rates of college completion, potentially improved employment outcomes, and research suggests an average increase in annual earnings compared to veterans who do not use their education benefits.

If you have more questions about your education benefits, don’t hesitate to reach out to us here at Benefits.com!
 Benefits.com Advisors
Benefits.com Advisors
With expertise spanning local, state, and federal benefit programs, our team is dedicated to guiding individuals towards the perfect program tailored to their unique circumstances.
Rise to the top with Peak Benefits!
Join our Peak Benefits Newsletter for the latest news, resources, and offers on all things government benefits.




















