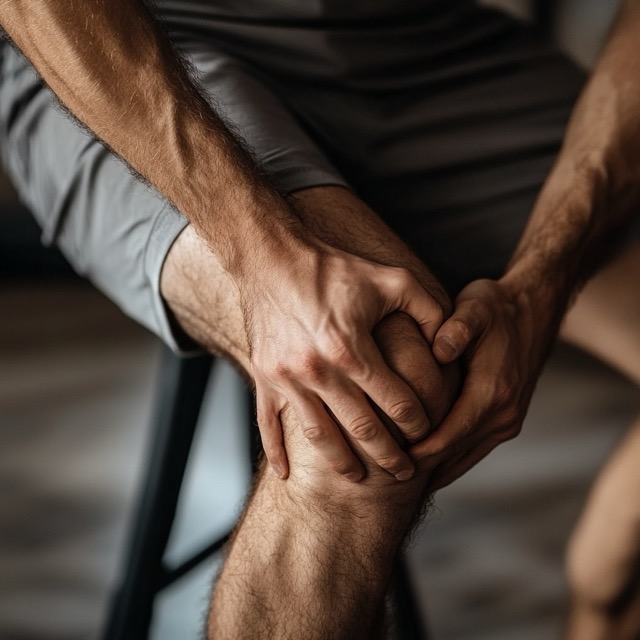
Tendonitis is a common condition that affects many veterans, causing pain and discomfort in various parts of the body. It occurs when a tendon, the thick cord that connects muscles to bones, becomes inflamed or irritated. This inflammation can result from repetitive motions, sudden injuries, or long-term overuse of a particular joint or muscle group.
For veterans, tendonitis often stems from the physical demands of military service. The rigorous training, carrying heavy equipment, and repetitive movements required in many military roles can put significant stress on tendons throughout the body. Understanding tendonitis and its impact on daily life is crucial for veterans seeking disability compensation through the Department of Veterans Affairs (VA).
Tendonitis can affect any tendon in the body, but it’s most commonly found in the shoulders, elbows, wrists, knees, and ankles. The condition can range from mild discomfort to severe pain that limits mobility and affects a veteran’s ability to work or perform daily activities.
Common Symptoms of Tendonitis

Veterans experiencing tendonitis may notice a variety of symptoms that can affect their quality of life and ability to function normally. Recognizing these symptoms is the first step in seeking proper treatment and potentially qualifying for VA disability benefits.
The most common symptoms of tendonitis include:
- Pain and tenderness near the affected joint, especially during movement
- Stiffness and reduced range of motion in the affected area
- Swelling or inflammation around the tendon
- A grating or crackling sensation when moving the affected joint
- Weakness in the affected limb or joint
- Pain that worsens with activity and improves with rest
It’s important to note that symptoms can vary depending on the location and severity of the tendonitis. For example, shoulder tendonitis might cause pain when reaching overhead, while Achilles tendonitis can make walking or running difficult.
If you’re experiencing these symptoms, especially if they persist for more than a few days or interfere with your daily activities, it’s crucial to seek medical attention. Early diagnosis and treatment can help prevent the condition from worsening and improve your chances of a full recovery.
Causes and Risk Factors of Tendonitis

Understanding the causes and risk factors of tendonitis is essential for veterans, as many aspects of military service can contribute to the development of this condition. Tendonitis typically results from a combination of factors, including repetitive motions, sudden injuries, and long-term stress on tendons.
Common causes of tendonitis in veterans include:
1. Repetitive movements: Military training and duties often involve repeating the same motions over extended periods, which can strain tendons.
2. Heavy lifting: Carrying heavy equipment, weapons, or supplies can put excessive stress on tendons.
3. Sudden increases in physical activity: Rapid changes in exercise intensity or duration, common during boot camp or deployment, can lead to tendon inflammation.
4. Poor posture or technique: Improper form during physical tasks can put unnecessary strain on tendons.
5. Direct injuries: Falls, impacts, or other traumas can damage tendons and lead to tendonitis.
Risk factors that may increase a veteran’s likelihood of developing tendonitis include:
- Age: As we get older, tendons become less flexible and more susceptible to injury.
- Certain medical conditions: Diseases like rheumatoid arthritis or diabetes can increase the risk of tendonitis.
- Occupational hazards: Jobs that involve repetitive motions or heavy lifting can contribute to tendon stress.
- Previous tendon injuries: Having a history of tendon problems can make you more prone to future issues.
Recognizing these causes and risk factors can help veterans take preventive measures and seek early treatment when symptoms arise. It’s also important information when establishing a service connection for VA disability claims related to tendonitis.
Diagnosing Tendonitis in Veterans
Proper diagnosis of tendonitis is crucial for veterans seeking VA disability benefits. The diagnostic process typically involves a combination of physical examination, medical history review, and potentially imaging studies. Understanding this process can help veterans prepare for their medical appointments and gather necessary evidence for their VA claims.
When diagnosing tendonitis, healthcare providers usually follow these steps:
1. Medical history: The doctor will ask about your symptoms, when they started, and any activities that worsen or alleviate the pain. For veterans, it’s important to mention any service-related activities that may have contributed to the condition.
2. Physical examination: The healthcare provider will examine the affected area, looking for signs of tenderness, swelling, or reduced range of motion. They may also ask you to perform specific movements to assess pain and functionality.
3. Imaging tests: In some cases, the doctor may order imaging studies to confirm the diagnosis or rule out other conditions. These may include:
4. X-rays: While they don’t show tendons directly, X-rays can help rule out other causes of pain, such as fractures or arthritis.
5. Ultrasound: This can provide real-time images of the tendon and surrounding tissues, helping to identify inflammation or tears.
6. MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging): This provides detailed images of soft tissues, including tendons, and can be useful in diagnosing more complex cases.
7. Additional tests: In some instances, the doctor may recommend blood tests to check for underlying conditions that could be contributing to tendon inflammation.
For veterans seeking VA disability benefits, it’s crucial to have a clear diagnosis from a qualified healthcare provider. This diagnosis, along with documentation of how the condition relates to your military service, will be essential in supporting your VA claim for tendonitis.
Types of Tendonitis and Associated VA Ratings
Tendonitis can affect various parts of the body, and the VA rates these conditions differently based on their location and severity. Understanding the types of tendonitis and their associated VA ratings can help veterans navigate the claims process more effectively.
1. Shoulder Tendonitis:
2. Often rated under Diagnostic Code 5201 for limitation of arm motion
3. Ratings range from 20% to 40% depending on the degree of limitation
4. VA disability rating for shoulder tendonitis can be up to 50% for the dominant arm
5. Elbow Tendonitis (Tennis Elbow):
6. Typically rated under Diagnostic Code 5206 or 5207 for limitation of flexion or extension
7. Ratings can range from 0% to 50% based on the severity of limitation
8. Knee Tendonitis (Patellar Tendonitis):
9. Often rated under Diagnostic Code 5260 or 5261 for limitation of flexion or extension
10. Ratings can range from 0% to 50% depending on the degree of limitation
11. Ankle Tendonitis (Achilles Tendonitis):
12. Usually rated under Diagnostic Code 5271 for limited motion of the ankle
13. Ratings are typically 10% for moderate limitation or 20% for marked limitation
14. Wrist Tendonitis:
15. Rated under Diagnostic Code 5215 for limitation of motion of the wrist
16. Typically receives a 10% rating for limited motion
It’s important to note that these ratings can vary based on individual circumstances and the specific impact of the condition on the veteran’s daily life and ability to work. The VA also considers factors such as pain, weakness, and fatigability when determining ratings.
For a comprehensive understanding of how the VA rates different types of tendonitis, veterans can refer to the Schedule for Rating Disabilities under 38 CFR § 4.71a.
Service Connection for Tendonitis
Establishing a service connection is crucial for veterans seeking VA disability benefits for tendonitis. A service connection demonstrates that your tendonitis is related to your military service, either directly or secondarily. There are several ways to establish this connection, and understanding them can significantly improve your chances of a successful claim.
Understanding Direct Service Connection
A direct service connection is the most straightforward way to link your tendonitis to your military service. To establish a direct service connection, you need to prove three elements:
1. A current diagnosis of tendonitis
2. Evidence of an in-service event, injury, or illness that could have caused or contributed to your tendonitis
3. A medical nexus (link) between your current tendonitis and the in-service event
For example, if you developed shoulder tendonitis during your service due to repetitive overhead lifting, and you can provide medical records showing treatment for shoulder pain during service, along with a current diagnosis and a doctor’s opinion linking the two, you may qualify for a direct service connection.
Secondary Service Connection for Tendonitis
Sometimes, tendonitis may develop as a result of another service-connected condition. This is known as a secondary service connection. To establish a secondary service connection, you need to show:
1. You have a current diagnosis of tendonitis
2. You have an existing service-connected condition
3. Medical evidence that your tendonitis is caused or aggravated by your service-connected condition
For instance, if you have a service-connected knee injury that causes you to alter your gait, leading to ankle tendonitis, you may be eligible for a secondary service connection for the ankle condition.
It’s important to gather comprehensive medical evidence and documentation to support your claim for service connection. This may include service medical records, post-service treatment records, and medical opinions from healthcare providers. VA Claims Insider offers resources and guidance on gathering evidence for your VA claim.
Remember, the key to a successful service connection claim is demonstrating the link between your military service and your current tendonitis condition. Be thorough in your documentation and don’t hesitate to seek assistance from veterans service organizations or VA-accredited representatives if you need help with your claim.
VA Disability Ratings for Tendonitis
Once a service connection is established for tendonitis, the VA assigns a disability rating based on the severity of the condition and its impact on your daily life and ability to work. Understanding how these ratings are determined can help you better navigate the claims process and ensure you receive the appropriate compensation.
VA disability ratings for tendonitis are typically based on the following factors:
1. Location of the affected tendon
2. Degree of limitation of motion
3. Pain and its impact on functionality
4. Frequency and severity of flare-ups
5. Impact on daily activities and employment
The VA uses the Schedule for Rating Disabilities to assign percentage ratings. For tendonitis, these ratings often fall under the musculoskeletal system category. Here’s a general overview of how ratings might be assigned:
- 0% rating: Symptoms are present but do not limit motion or function significantly
- 10% rating: Mild limitation of motion or function, with pain on movement
- 20% rating: Moderate limitation of motion or function, with pain that impacts daily activities
- 30% or higher: Severe limitation of motion or function, significant pain, and substantial impact on daily life and ability to work
It’s important to note that these percentages can vary depending on the specific type of tendonitis and the affected body part. For instance, shoulder tendonitis might be rated differently than Achilles tendonitis due to the different functions of these body parts.
Additionally, the VA considers the concept of “painful motion” when assigning ratings. Even if your range of motion is not significantly limited, you may still qualify for a compensable rating if you experience pain throughout the range of motion.
The VA also takes into account factors such as:
- Flare-ups and their frequency
- Additional limitation during flare-ups
- Fatigue, weakness, and lack of endurance
- Impact on your ability to perform occupational tasks
For a more detailed understanding of how your specific type of tendonitis might be rated, it’s helpful to review the VA’s Schedule for Rating Disabilities and consult with a veterans service organization or VA-accredited representative.
Remember, if you believe your tendonitis has worsened since your last VA evaluation, you have the right to file for an increased rating. Keeping detailed records of your symptoms, treatment, and how the condition affects your daily life can be invaluable in supporting your claim for a higher rating.
How to Apply for a Tendonitis VA Rating

Applying for a VA disability rating for tendonitis involves several steps. Understanding this process can help you navigate it more effectively and increase your chances of a successful claim. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to apply:
1. Gather necessary documentation:
- Medical records showing diagnosis and treatment of tendonitis
- Service records that may show related injuries or complaints
- Statements from you, family members, or fellow service members about how tendonitis affects your daily life
2. Complete VA Form 21-526EZ:
- This is the Application for Disability Compensation and Related Compensation Benefits
- You can find this form on the VA’s website or at your local VA office
3. Submit your claim:
- You can submit your claim online through the VA’s eBenefits portal
- Alternatively, you can mail your completed form to your local VA regional office
- You can also submit your claim in person at a VA office
4. Attend a C&P Exam:
- After reviewing your claim, the VA may schedule you for a Compensation and Pension (C&P) exam
- This exam is crucial for determining your disability rating, so be prepared to discuss your symptoms in detail
5. Wait for the VA’s decision:
- The VA will review all evidence and make a decision on your claim
- This process can take several months, so patience is key
6. Review the decision:
- If you disagree with the VA’s decision, you have the right to appeal
- Consider seeking assistance from a veterans service organization if you need to appeal
Remember, the key to a successful claim is providing thorough and accurate information. Be honest about your symptoms and how they impact your daily life. Don’t downplay the effects of your condition, but also avoid exaggerating.
For more detailed information on the application process, you can visit the VA’s disability benefits page.
Tips for a Successful VA Claim
Filing a successful VA claim for tendonitis requires attention to detail and thorough preparation. Here are some tips to help improve your chances of a favorable outcome:
1. Be specific and detailed:
- Clearly describe how your tendonitis affects your daily activities and work
- Provide specific examples of limitations you experience due to the condition
2. Keep a symptom journal:
- Document flare-ups, pain levels, and how symptoms impact your daily life
- This can provide valuable evidence for your claim
3. Get buddy statements:
- Statements from fellow service members, family, or friends can corroborate your condition and its effects
4. Obtain a medical nexus letter:
- A letter from your doctor linking your tendonitis to your military service can significantly strengthen your claim
5. Be consistent:
- Ensure that your statements to the VA match your medical records and other documentation
6. Don’t miss deadlines:
- Respond promptly to any requests from the VA for additional information
7. Consider getting help:
- Veterans Service Organizations (VSOs) or VA-accredited representatives can provide valuable assistance with your claim
8. Prepare for your C&P exam:
- Review your medical history and be ready to discuss your symptoms in detail
- Be honest about your pain and limitations
- Include all medical records, even those that may seem only tangentially related
- 9. Follow up:
Don’t be afraid to check on the status of your claim - If you haven’t heard anything in a while, contact the VA for an update
Remember, the VA claims process can be complex and time-consuming. Patience and persistence are key. If your initial claim is denied, don’t give up. Many veterans succeed on appeal or by submitting a new claim with additional evidence.
For more tips and resources on filing a successful VA claim, check out VA Claims Insider.
Appealing a Denied VA Claim for Tendonitis
If your VA claim for tendonitis is denied or you receive a lower rating than you believe is appropriate, you have the right to appeal the decision. Understanding the appeals process can help you navigate this challenging situation more effectively.
The VA appeals process includes several options:
1. Supplemental Claim:
2. You can file a Supplemental Claim if you have new and relevant evidence that wasn’t considered in the original decision
3. This option allows you to submit additional evidence to support your claim
4. Higher-Level Review:
5. You can request a Higher-Level Review if you believe there was an error in the initial decision
6. A senior VA reviewer will take a fresh look at your claim
7. Board Appeal:
8. You can appeal directly to the Board of Veterans’ Appeals
9. This option allows you to submit additional evidence and potentially have a hearing with a Veterans Law Judge
When appealing a denied claim or seeking a higher rating for tendonitis, consider the following tips:
- Review the denial letter carefully to understand why your claim was denied or why you received a lower rating
- Gather any new evidence that addresses the reasons for denial
- Consider obtaining additional medical opinions that support your claim
- Be prepared to explain how your tendonitis impacts your daily life and ability to work
- Don’t miss any deadlines—the appeals process has strict time limits
Remember, appealing a VA decision can be a complex process. It may be helpful to seek assistance from a Veterans Service Organization (VSO) or a VA-accredited attorney who can guide you through the process and help strengthen your appeal.
Begin your journey to benefits today by taking our quiz at Benefits.com to see what you’re eligible for, and how we can help you.
 Benefits.com Advisors
Benefits.com Advisors
With expertise spanning local, state, and federal benefit programs, our team is dedicated to guiding individuals towards the perfect program tailored to their unique circumstances.
Rise to the top with Peak Benefits!
Join our Peak Benefits Newsletter for the latest news, resources, and offers on all things government benefits.




















