PTSD is a serious condition that many veterans spend their lives dealing with, and there’s a lot more complexity to it than meets the eye. PTSD can give rise to various medical conditions including anxiety disorders, depression, substance abuse, and sleep disorders. We’re going to delve into the connection between these conditions and PTSD, explaining how PTSD can exacerbate or lead to their development. Here’s what you should know about secondary conditions that may arise from PTSD, how the Social Security Administration (SSA) can assist, and the process to qualify for the benefits you medically, ethically, and legally deserve.
Anxiety

Anxiety disorders are common conditions secondary to PTSD, disrupting an individual’s daily life and overall well-being. When someone experiences a traumatic event, such as a life-threatening situation, physical or emotional abuse, or witnessing a tragedy, it can trigger an intense and persistent fear response. This heightened state of arousal and distress can manifest in various disorders.
GAD
One common anxiety disorder associated with PTSD is generalized anxiety disorder (GAD), characterized by excessive worry and apprehension about a wide range of events and situations. Individuals may constantly feel on edge, have difficulty concentrating, experience muscle tension, and struggle with sleep disturbances. Another anxiety disorder linked to PTSD is panic disorder, which leads to recurrent panic attacks accompanied by intense physical symptoms such as heart palpitations, shortness of breath, and a sense of impending doom.
Social Anxiety
Another secondary anxiety disorder of PTSD is social anxiety disorder, where individuals experience extreme fear and avoidance of social situations due to concerns about being judged or humiliated, and specific phobias triggered by stimuli associated with the traumatic event. This anxiety disorder can significantly impair an individual’s ability to function, maintain relationships, and engage in normal daily activities.
Depression
PTSD can also give rise to depressive disorders, compounding the emotional toll of the traumatic event. Depression associated with PTSD is often referred to as “secondary depression” because it stems from the experience and aftermath of the trauma. The impact of PTSD on one’s life, including feelings of helplessness, guilt, and intrusive memories, can contribute to the development of depressive symptoms and overall decline of mental health.
Depression disorders caused by PTSD share common symptoms with major depressive disorder. Individuals may experience persistent sadness, loss of interest or pleasure in activities, changes in appetite and sleep patterns, fatigue, difficulty concentrating, feelings of worthlessness or guilt, and thoughts of self-harm or suicide. These symptoms can be pervasive and disrupt the person’s ability to function and engage in daily life.
Sleep Disorders

Sleep disorders caused by PTSD can exacerbate other symptoms, such as irritability, difficulty concentrating, and heightened emotional reactivity. The lack of quality sleep also hinders the brain’s ability to process and regulate emotions effectively, leading to a vicious cycle of sleep disturbances and increased PTSD symptoms.
Sleep apnea can be considered both a sleep disorder and a respiratory disorder, and obstructive sleep apnea is a common secondary condition to PTSD. Insomnia is another prevalent sleep disorder experienced by individuals with PTSD. They may struggle with falling asleep, staying asleep, or experiencing non-restorative sleep. Nightmares are another distressing symptom, characterized by vivid and disturbing dreams related to the traumatic event. These nightmares can cause individuals to wake up in a state of fear and anxiety, making it difficult to go back to sleep.
Substance Abuse
PTSD can contribute to the development of substance abuse problems, as individuals often turn to drugs or alcohol to cope with the distressing symptoms and emotions associated with their traumatic experiences and secondary trauma. Substance abuse can temporarily alleviate feelings of anxiety, depression, and hyperarousal commonly experienced in PTSD.
Individuals with PTSD may resort to self-medicating with substances as a way to numb their emotional pain or to escape intrusive memories and flashbacks. Unfortunately, relying on substances as a coping mechanism can lead to a cycle of addiction, worsening overall well-being and exacerbating PTSD symptoms.
Substance abuse caused by PTSD poses significant risks to physical and mental health, as it can lead to a range of negative consequences, including impaired judgment, relationship problems, occupational difficulties, and health complications. It is crucial to recognize the link between PTSD and substance abuse and seek integrated treatment that addresses both issues simultaneously.
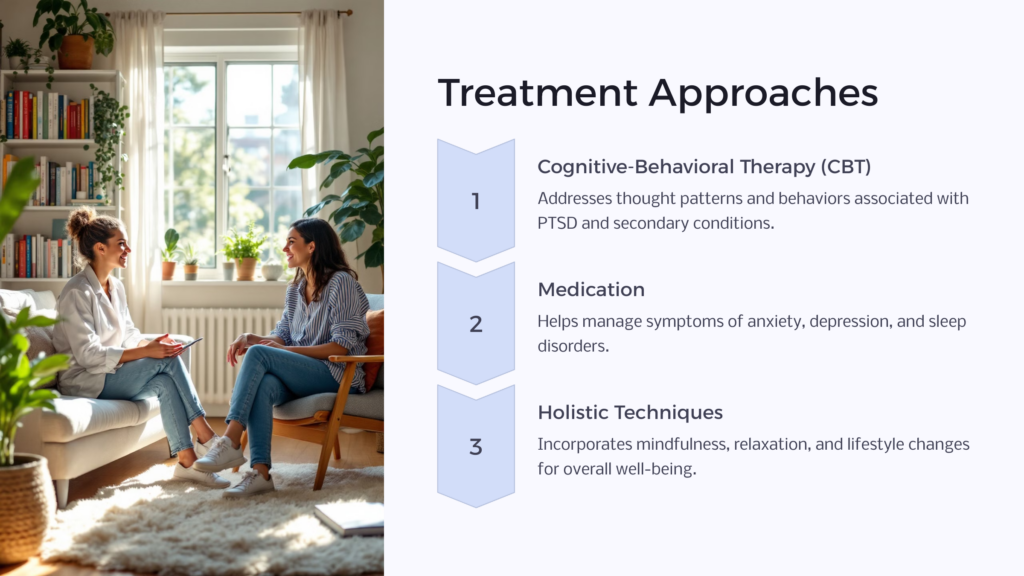
Therapeutic approaches such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), medication, and holistic techniques can be effective in addressing the symptoms associated with PTSD. Whether it is managing anxiety, depression, sleep disturbances, or substance abuse, a comprehensive and integrated approach is key to promoting healing and enhancing the quality of life for individuals impacted by PTSD.
Help from SSA

The SSA offers social security for mental disorders, including those secondary to PTSD. By offering Social Security Disability Insurance (SSDI) benefits, the SSA aims to provide financial assistance to individuals who are unable to work due to their disabilities.
To receive SSDI benefits related to conditions secondary to PTSD, certain eligibility criteria must be met. The severity of impairments, duration of conditions, and limitations on work capacity are all considered. By understanding these criteria, individuals can determine if they qualify for SSDI benefits and what steps they need to take.
Veterans Affairs (VA) also provides help to veterans suffering from PTSD. VA form 21-0781 is put in place to help Veterans with PTSD get the VA disability help they need. Once your VA claim is submitted, they will review your application and give your medical condition a disability rating, which will affect how much you receive in VA disability benefits.
Applying for SSDI benefits with PTSD and related conditions can be overwhelming. Therefore, seeking legal representation or advocacy is often beneficial. Professional assistance, such as disability lawyers and advocates, during the application and appeals process can be extremely helpful in guiding individuals through the stress and complexities of the veteran benefits system.
For more information and assistance, contact us at Benefits.com, where we’ll advise you on the application process!
 Benefits.com Advisors
Benefits.com Advisors
With expertise spanning local, state, and federal benefit programs, our team is dedicated to guiding individuals towards the perfect program tailored to their unique circumstances.
Rise to the top with Peak Benefits!
Join our Peak Benefits Newsletter for the latest news, resources, and offers on all things government benefits.




















