Agent Orange, a herbicide used during the Vietnam War, has left a long-lasting impact on the health of veterans who were exposed to it. One of the serious health conditions linked to Agent Orange exposure is Ischemic Heart Disease (IHD). This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of Agent Orange Ischemic Heart Disease, VA Disability Compensation, and the process of filing a claim for this condition.
What is Ischemic Heart Disease (IHD)?

Ischemic Heart Disease (IHD), often referred to as coronary artery disease, is a condition that occurs when the blood supply to the heart muscle is reduced due to the narrowing of the coronary artery, which is a potential heart problem. This reduced blood flow, and even high blood pressure can lead to chest pain (angina) and, in severe cases, a heart attack, or even heart failure.
Coronary Artery Disease is one of the most frequent causes of heart failure. Thus, coronary artery disease should be taken seriously as a potentially life-threatening heart condition or potentially be another risk factor for another heart health problem in the cardiovascular system. Such risk can include, but are not limited to, an ischemic stroke, ventricular dysfunction, and other cardiovascular outcomes.
The Link Between Agent Orange and IHD

Agent Orange is a powerful herbicide that was used during the Vietnam War to defoliate forests and destroy crops. Unfortunately, it was later discovered that exposure to Agent Orange could have severe health consequences in the cardiovascular system for those who came into contact with it. In 2010, the Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) recognized a connection between exposure to Agent Orange and the development of IHD in veterans.
Qualifying for VA Benefits for Agent Orange-Related IHD

To be eligible for VA disability benefits, especially Ischemic Heart Disease benefits related to Agent Orange exposure, a veteran must meet the following criteria:
- Service in Vietnam or along the demilitarized zone in Korea: Veterans who served in Vietnam or along the Korean demilitarized zone between 1962 and 1975 are presumed to have been exposed to Agent Orange.
- Diagnosis of IHD: The veteran must have a medical diagnosis of IHD or a related heart condition.
- Disability rating: The VA will evaluate the severity of the IHD and assign a disability rating based on the impact it has on the veteran’s ability to work and carry out daily activities.
VA Disability Compensation Overview
- What is VA Disability Compensation?
VA Disability Compensation is a financial benefit provided to veterans who have service-connected disabilities. These disabilities can be physical or mental health conditions that were incurred or aggravated during military service. The purpose of this compensation is to provide financial support to veterans who may be unable to work or face other challenges due to their service-connected disabilities, whether short term or long term disability.
- How Is VA Disability Compensation Calculated?
The VA uses a rating system to determine the level of disability compensation a veteran is eligible to receive. Disability ratings range from 0% to 100%, with higher ratings corresponding to more severe disabilities. The VA takes into account the impact of the disability on the veteran’s ability to work and perform daily activities.
- Benefits of VA Disability Compensation for IHD
For a Vietnam veteran with Agent Orange-related IHD, VA Disability Compensation can provide financial support to help cover medical expenses and support their overall well-being. The compensation amount depends on the VA disability rating it is assigned. In some cases, veterans may also be eligible for additional benefits, such as special monthly compensation or aid and attendance benefits.
Filing a Claim for Ischemic Heart Disease
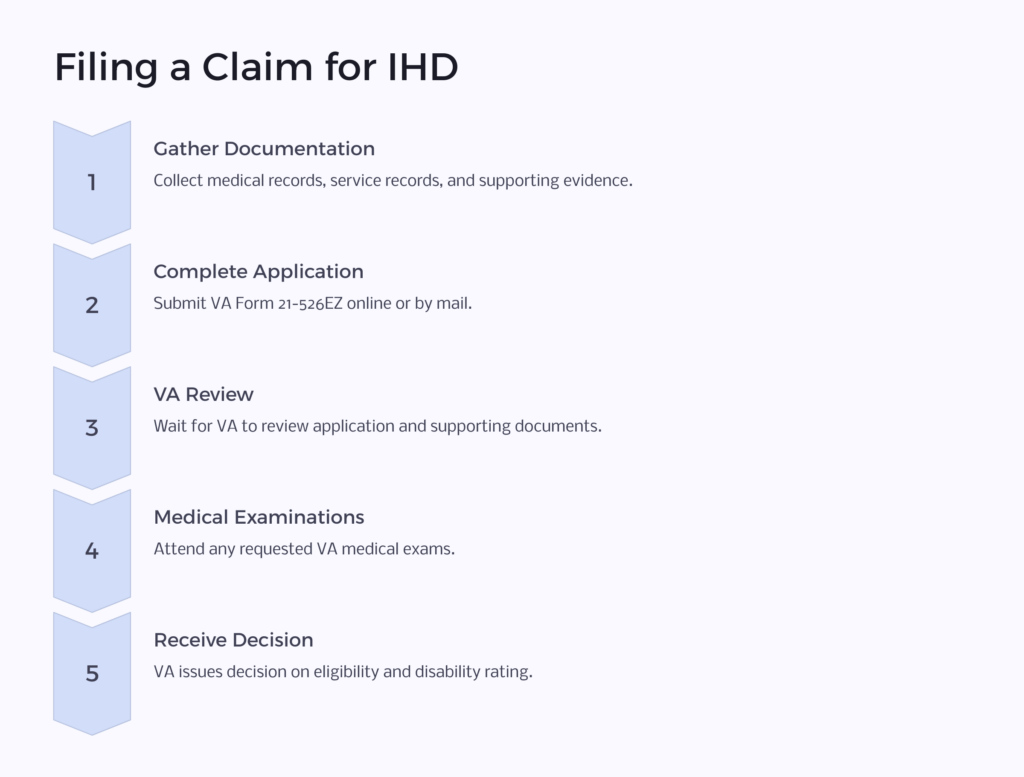
Step 1: Gather Documentation
Before filing a VA disability claim for Agent Orange-related IHD, it’s crucial to gather all relevant documentation. This includes reports on your medical condition, military service records, as a Vietnam veteran and any other evidence that supports your claim. Your medical records should clearly indicate your IHD diagnosis and its relationship to Agent Orange exposure.
Step 2: Complete the Application
To apply for VA Disability Compensation, you’ll need to complete VA Form 21-526EZ, which is the Application for Disability Compensation and Related Compensation Benefits. You can submit this form online through the VA’s eBenefits portal or by mailing a paper copy to your local VA regional office.
Step 3: Await VA Review
Once your claim is submitted, the VA will review your application and supporting documentation. This process can take some time, and it’s essential to be patient.
Step 4: Attend Medical Examinations
In some cases, the VA may request that you undergo a medical examination to assess the severity of your IHD. It’s important to attend these examinations as they can significantly impact the outcome of your VA disability claim.
Step 5: Receive a Decision
After reviewing your claim and supporting evidence, the VA will issue a decision regarding your eligibility for VA Disability Compensation for Agent Orange-related IHD. If approved, you will receive a disability rating and information about your compensation.
Average Disability Rates:
The amount of compensation a veteran receives is determined by the VA’s rating system, which assigns a percentage to the disability based on its severity. These percentages range from 0% to 100%, in increments of 10%. The higher the percentage, the more compensation the veteran is eligible to receive.
In September 2021, the VA disability ratings, ranging from 10% to 100%, are as follows:
- 10% disability rating: $144.14 per month
- 20% disability rating: $284.93 per month
- 30% disability rating: $441.35 per month
- 40% disability rating: $635.77 per month
- 50% disability rating: $905.04 per month
- 60% disability rating: $1,146.39 per month
- 70% disability rating: $1,444.71 per month
- 80% disability rating: $1,679.35 per month
- 90% disability rating: $1,887.18 per month
- 100% disability rating: $3,146.42 per month
It’s important to note that these rates can change over time due to inflation and other factors. Veterans should always check the VA’s official website or consult with a veterans service officer to get the most up-to-date information on disability compensation rates.
How to Maximize Disability Benefits
Maximizing disability benefits requires careful consideration and attention to detail. Here are some strategies to help veterans make the most of their VA disability benefits:
- Seek a Fair Rating: Ensure that your heart condition is assigned the most accurate VA disability rating. This often involves providing comprehensive evidence and documentation of how your medical condition affects your daily life.
- File for Multiple Disabilities: If you have more than one service-connected disability, be sure to file claims for each condition separately. This can result in a higher combined disability rating and greater compensation.
- Consider Secondary Conditions: Some disabilities can lead to secondary conditions. If your service-connected disability has caused other health problems, you may be eligible for additional compensation.
- Stay Informed: Keep track of changes in your health and how your service-connected disabilities are affecting you. If your condition worsens, you can file for an increased rating.
- Appeal if Necessary: If you disagree with the VA’s decision on your disability rating, don’t hesitate to appeal. Many veterans win higher ratings on appeal.
Additional Veterans Benefits and Resources
In addition to disability compensation, veterans may be eligible for various other VA benefits and resources. Here are some examples:
- VA Healthcare: Veterans with service-connected disabilities often qualify for free or low-cost healthcare through the VA. This includes access to doctors, specialists, and prescription medications.
- Vocational Rehabilitation and Employment (VR&E): VR&E programs help veterans with service-connected disabilities prepare for, find, and keep suitable jobs. They can provide education and training, job-seeking skills, and other support.
- Educational Benefits: The GI Bill offers educational assistance to veterans, including tuition and housing allowances. Some veterans with service-connected disabilities may be eligible for additional educational benefits through programs like the Post-9/11 GI Bill.
- Home Loans: The VA provides home loan guarantees, making it easier for veterans to buy or refinance a home. Disabled veterans may be eligible for additional benefits in this regard.
- Adaptive Housing Grants: Veterans with certain service-connected disabilities that limit mobility may be eligible for grants to make their homes more accessible.
Understanding the VA rating system, maximizing benefits, and exploring additional resources are crucial for veterans seeking the support they’ve earned through their service to our country. While this article provides valuable information on heart health and disability benefits, veterans are encouraged to work with veteran service organizations and experts to navigate the complexities of the VA system and ensure they receive the veteran benefits they deserve. Remember that VA policies and rates may change over time, so staying informed is essential to making the most of your benefits. If you have more questions about disability payment, contact us at Benefits.com.
 Benefits.com Advisors
Benefits.com Advisors
With expertise spanning local, state, and federal benefit programs, our team is dedicated to guiding individuals towards the perfect program tailored to their unique circumstances.
Rise to the top with Peak Benefits!
Join our Peak Benefits Newsletter for the latest news, resources, and offers on all things government benefits.