Spinal stenosis is a degenerative condition that affects the spinal canal, resulting in the narrowing of the passageways through which nerves in the spinal cord travel. As a long term disability, spinal stenosis can significantly impact a person’s quality of life, causing chronic pain, numbness, and weakness. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and daily challenges faced by individuals with spinal stenosis is crucial in fostering empathy and promoting a supportive environment.

Spinal stenosis often develops due to age-related changes in the spine, such as osteoarthritis or the formation of bone spurs. These changes lead to the narrowing of the spinal canal, compressing the spinal nerve, and resulting in a range of debilitating symptoms. Individuals with spinal stenosis commonly experience persistent chronic back pain, radiating severe pain down the legs (sciatica), neck pain, muscle weakness, numbness, and tingling sensations. The severity and specific spinal stenosis symptoms can vary depending on the location and extent of the spinal canal narrowing.
Living with spinal stenosis presents numerous challenges for individuals in their daily lives. Simple tasks like walking, standing, or sitting for prolonged periods can become excruciatingly painful. The chronic pain and discomfort can limit mobility, making it difficult to perform routine activities, such as household chores or even personal hygiene tasks. The loss of sensation and muscle weakness may affect balance, making walking and navigating stairs hazardous. Moreover, individuals with severe cases of spinal stenosis may find it challenging to maintain an active lifestyle, participate in recreational activities, or pursue their careers.

Is Spinal Stenosis a Permanent Disability?
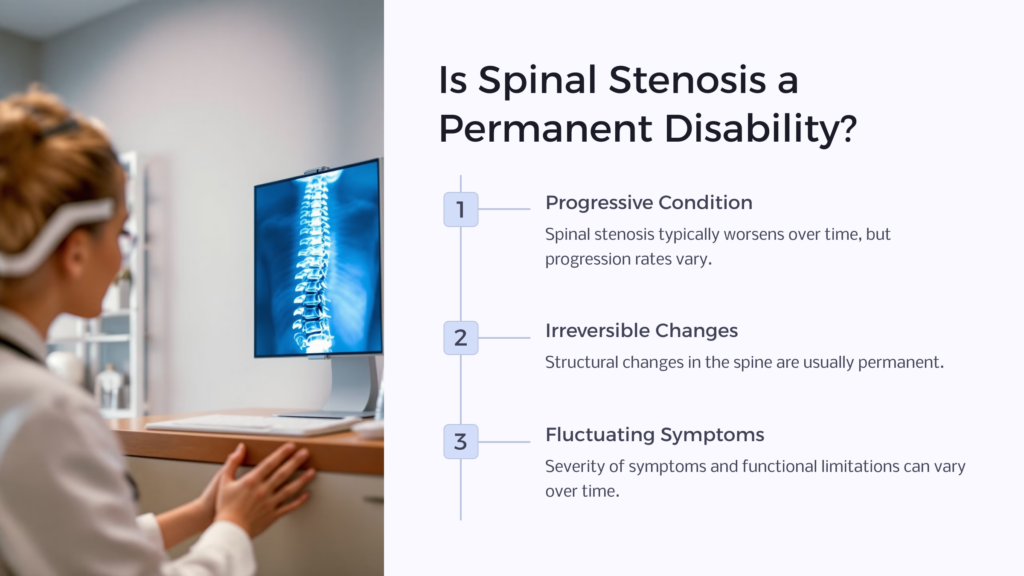
Spinal stenosis is generally considered a progressive condition, meaning it tends to worsen over time. While the rate of progression can vary from person to person, it is important for individuals with spinal stenosis to understand the long-term outlook of their medical condition and manage their expectations accordingly. Spinal stenosis permanence and prognoses depends on the person and their circumstances.
Spinal stenosis can be considered a permanent disability in many cases. The structural changes in the spine that cause the narrowing of the spinal canal are typically irreversible. However, it is important to note that the severity of symptoms and functional limitations can fluctuate over time. Some individuals may experience periods of relative stability or even temporary improvement, while others may notice a gradual decline in their condition.
What Factors Influence Spinal Stenosis Benefits?
Social Security disability insurance takes into account several factors when evaluating spinal stenosis, including medical evidence, diagnostic imaging results, clinical findings, and the impact of the medical condition on an individual’s daily activities. They assess the severity of symptoms, such as pain, numbness, weakness, and limitations in mobility, and consider the resulting functional limitations, including the ability to stand, walk, sit, and perform daily tasks.
The disability rating assigned to spinal stenosis depends on the extent to which the condition significantly impacts an individual’s ability to engage in substantial gainful activity. This rating directly influences eligibility for social security disability benefits.
It is important for individuals with spinal stenosis seeking disability benefits to provide comprehensive medical documentation, including CT scan or other imaging results, treatment records, and other medical record reports from healthcare professionals. Such evidence can substantiate the severity of their condition and the resulting functional limitations, increasing the likelihood of a favorable evaluation for SSDI benefits.
What Are the Criteria for Qualifying?

Individuals with spinal stenosis who experience significant functional limitations and are unable to engage in substantial gainful activity may be eligible for various Social Security benefits. Understanding the criteria for eligibility, the application process, and the types of benefits available can provide individuals with spinal stenosis with valuable financial and medical support.
To qualify for Social Security benefits, individuals must meet the eligibility criteria outlined by the Social Security Administration (SSA). This includes having a medically determinable impairment, such as spinal stenosis, that is expected to last for at least 12 months or result in death. The condition must also significantly limit the individual’s ability to perform work-related activities.
The application process typically involves gathering a comprehensive medical record, including diagnoses, treatment records, and supporting evidence of functional limitations. The SSA will assess the medical evidence provided, conduct a thorough evaluation, and determine eligibility for SSDI benefits. Preparing for your disability interview by organizing all your medical evidence and applying correctly will give you the best chance.
What Treatment Options are Available to Treat Spinal Stenosis?
Treatment options for spinal stenosis may include non-surgical interventions such as physical therapy, which can help strengthen the muscles supporting the spine and improve flexibility. Pain management techniques, including medication, epidural steroid injections, or nerve blocks, may also be employed to alleviate discomfort.
Lifestyle modifications play a crucial role in managing spinal stenosis. Maintaining a healthy weight reduces stress on the spine, and regular exercise, such as low-impact activities like swimming or walking, can help improve mobility and reduce pain. Using adaptive aids, such as canes or braces, can provide stability and support during daily activities.
Self-care strategies are equally important. Practicing good posture, avoiding activities that exacerbate symptoms, and implementing proper body mechanics can help minimize strain on the spine. Applying heat or cold packs to affected areas and engaging in relaxation techniques like yoga or meditation may also provide relief.
By combining appropriate medical treatments, lifestyle adjustments, and self-care strategies, individuals with spinal stenosis can effectively manage their condition, reduce pain, improve function, and enhance their overall well-being. Consulting with healthcare professionals and seeking personalized guidance can further optimize the treatment approach for each individual.
Spinal stenosis can have a significant impact on a person’s daily life, and individuals with this condition may be eligible for disability benefits. By understanding what spinal stenosis entails, its long-term prognosis, the evaluation process for disability benefits, and the available social security benefits, individuals can make informed decisions and seek the support they need. For more information and help with your application, please contact us at Benefits.com.
 Benefits.com Advisors
Benefits.com Advisors
With expertise spanning local, state, and federal benefit programs, our team is dedicated to guiding individuals towards the perfect program tailored to their unique circumstances.
Rise to the top with Peak Benefits!
Join our Peak Benefits Newsletter for the latest news, resources, and offers on all things government benefits.




















