Sometimes a disability comes out of the blue without notice. Even if it’s a temporary disability, such as a broken bone or concussion, the injury or condition can keep you from working for a significant period of time.
Fortunately, there are temporary disability benefits programs in place that can help you cover wage loss or loss of earning capacity from a short-term disability.
In this post, we’ll explore what temporary disability benefits are, as well as answers to common questions about qualifying and applying for these benefits.
What Are Temporary Disability Benefits?
Temporary disability benefits are financial assistance provided to those who are temporarily unable to work due to a short-term disability. These benefits help replace a portion of lost income during the period you’re unable to work.
A temporary or short-term disability is an injury, illness, or medical condition that’s expected to improve in more than a month but less than a year.
If you acquire a short-term disability, you may wonder if you qualify for Supplemental Security Income (SSI) or Social Security Disability Insurance (SSDI).
Both programs are designed to provide benefits to those whose conditions are long-term (expected to last 12 months or longer) or result in death. Since a temporary disability is defined as a condition that can improve in less than a year, you cannot receive temporary SSI or SSDI benefits.
How To Get Temporary Disability Benefits
While you won’t qualify for SSI or SSDI benefits with a temporary disability, you can still get financial assistance from other programs. Here are some common ways to get temporary disability benefits:
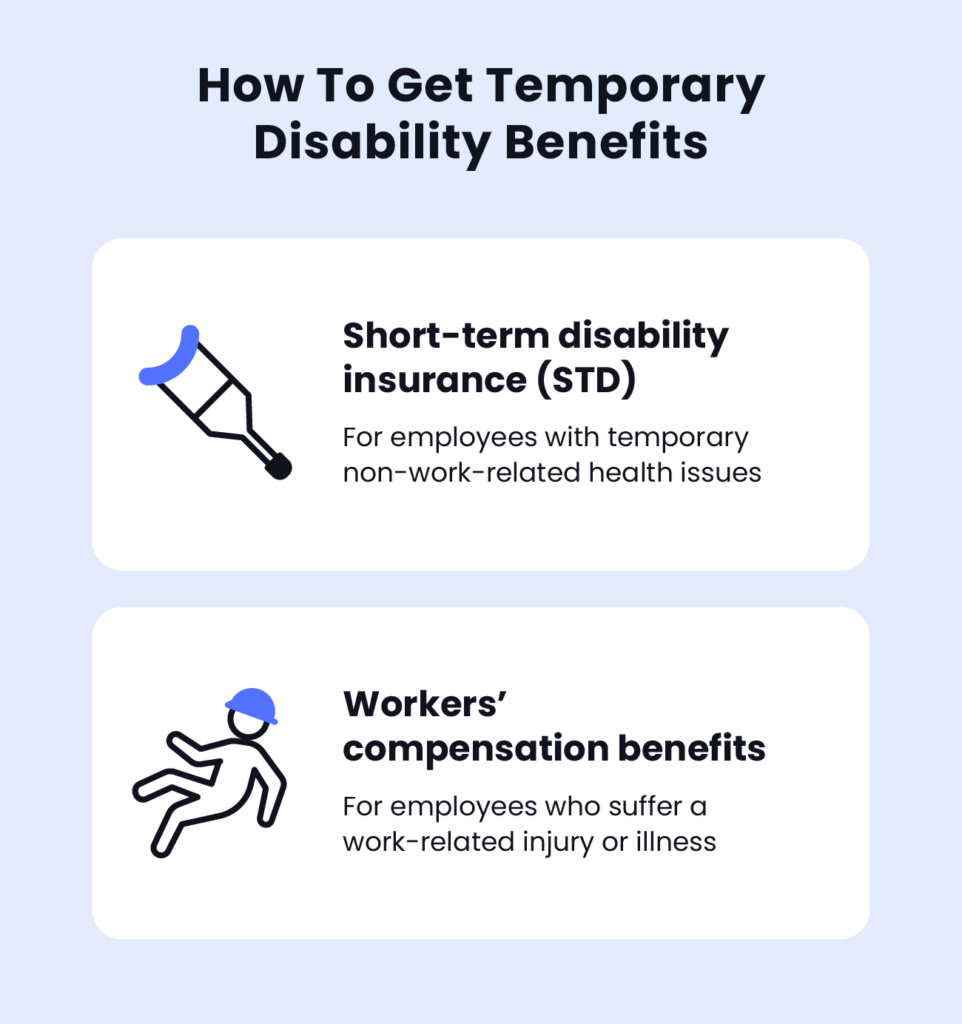
Short-Term Disability Insurance (STD)
Short-term disability insurance is typically offered through employers or purchased individually. It provides income replacement for employees who are temporarily unable to work due to a non-work-related illness, injury, or medical condition.
Some U.S. states and territories, such as Rhode Island, New York, Hawaii, and Puerto Rico, have laws that require employers to extend the temporary disability insurance program to individuals with short-term disabilities who the federal government does not cover.
Workers’ Compensation Benefits
Workers’ compensation benefits are provided to employees who suffer a work-related injury or illness. These benefits typically include coverage for medical expenses related to the injury or illness and a portion of lost wages during the recovery period.
What Qualifies as a Short-Term Disability?
Non-occupational injuries, major surgery, chronic conditions, and illnesses expected to improve in more than a month but less than one year qualify as a short-term disability.
Your doctor or a qualified medical examiner determines the severity of your illness and recommends a period of recovery or restricted activity. The employer, Social Security Administration, and the insurance provider then use the medical specialist’s evaluation to learn about the disability rating, or “partial disability” status.
On the other hand, workers’ compensation covers any bodily harm or physical impairment on the job. To determine how much workers’ compensation you’re eligible for, you’ll fall into one of two categories:
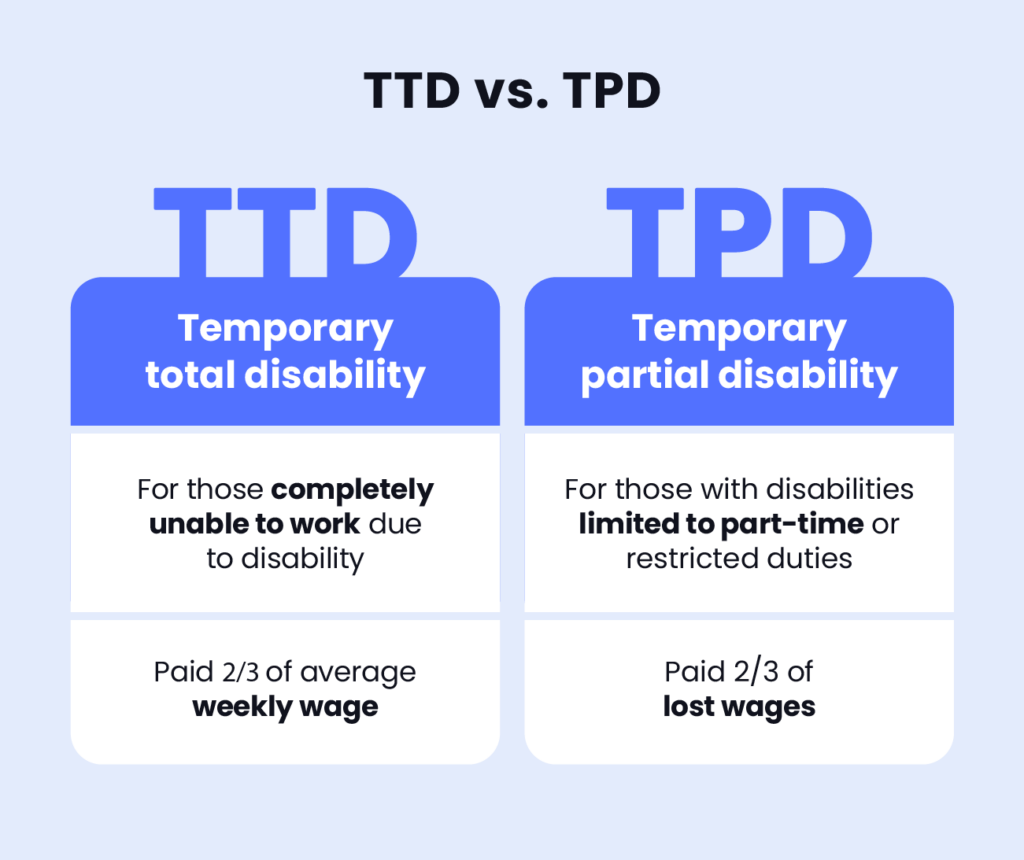
- Temporary total disability (TTD): This is for those completely unable to work due to disability. TTD benefits amount to two-thirds of your pre-tax income before your disability.
- Temporary partial disability (TPD): This is for those with disabilities limited to part-time or restricted duties. TPD benefits amount to two-thirds of your lost wages, capped by your maximum TD rate. Lost wages are calculated as the difference between your average weekly wages and what you earn while working part time.
Examples of Temporary Disability
Unexpected circumstances may hinder an individual’s ability to work for a short time. During this period, where employment TTD benefits and paid family leave are a cash flow solution, your full recovery becomes the foremost priority before resuming your regular work schedule or performing any job duties again.
Significant factors that can cause temporary disability include:
- Fractures or broken bones
- Cuts, burns, or other physical wounds
- Sprains or strains
- Pregnancy
- Back problems
- Dislocations
- Shock or trauma
- Surgery
- Visual disorders
- COVID-19, quarantine, or isolation

How Do You Know When You’ve Been Approved for Short-Term Disability Insurance?
After filing a claim with the insurer or the state and successfully undergoing a review for short-term disability, you are officially eligible to aid in rehabilitating your physical or mental health. It is important to note that the latency period can vary by insurer.
Within 14-45 days, a standard insurance company will notify you of their decision to approve you for a three- to six-month temporary disability insurance policy.
Regardless of how long the disability lasts, you are entitled to pay the premiums, and the insurer is responsible for covering all TTD benefits due to you.
How Much Cash Assistance Can You Receive on Short-Term Disability Insurance?
Short-term disability insurance gives you a cash benefit depending on your longevity with the company. Your employer-sponsored plan typically pays 50% to 60% of your weekly wages, so you can use the money to get back on your feet.
You can alternatively get your entire paycheck from another broker or protection policy to make up the difference. And where the state mandates short-term disability insurance, authorities may regulate the percentage of your salary they can pay.
How Long Does Short-Term Disability Insurance Last?
How long short-term disability insurance lasts varies depending on the policy. Some policies offer coverage for up to a year, while others may have shorter payout windows, such as six months or three months.
While some income safeguard packages will have a decreasing payout after a certain period, others will have a steady reimbursement that does not change in the face of a set time frame. There’s no sweet spot in between. So, to avoid surprises it’s important for individuals purchasing these policies to thoroughly review the details in the insurance contract.
How To Get Short-Term Disability Insurance
You can get short-term disability insurance a few different ways. Here are some popular methods that you can use to get short-term disability insurance:
- Apply through your employee benefits. Utilize the short-term disability coverage provided by your employer as part of your employee benefits package.
- Purchase an individual plan through your employer. If your workplace does not provide STD coverage, you may be able to buy it as a voluntary benefit.
- Purchase an individual plan through an insurance provider. If there’s no STD coverage provided by your employer, you can purchase an individual plan through an insurance provider.

What To Keep in Mind Before Applying for Short-Term Disability
There are a few things to keep in mind before applying for benefits with a temporary disability:
- Document your illness or injury: Ensure you have documented medical evidence that confirms your disability to support your claim for STD benefits.
- Understand your policy’s elimination period: Each STD policy has a requirement for how long you must be out of work before you can claim short-term disability, known as an elimination period. This is typically seven to 30 days, depending on your policy.
- Understand your rights and responsibilities: Familiarize yourself with any obligations related to reporting changes in your condition, attending medical evaluations, or participating in vocational rehabilitation programs.
- Prepare for possible denials: Be aware that STD claims may be initially denied. Understand the appeals process outlined by your insurance provider or employer. Gather any additional evidence or documentation to support your claim in case of a denial.
- Seek guidance if needed: If you have questions or concerns about the STD claims process, consider seeking guidance from a legal or financial advisor or contacting your state’s department of labor or insurance commissioner for assistance.
Benefits.com Can Help You Maximize Your Potential Benefits
While government benefit programs typically cater to individuals with long-term disabilities, you may qualify for benefits if your disability lasts over 12 months. At Benefits.com, we aim to help all U.S. residents navigate government programs effectively. Discover your eligibility with our Benefits Quiz to access the best benefits for your situation.
 Benefits.com Advisors
Benefits.com Advisors
With expertise spanning local, state, and federal benefit programs, our team is dedicated to guiding individuals towards the perfect program tailored to their unique circumstances.
Rise to the top with Peak Benefits!
Join our Peak Benefits Newsletter for the latest news, resources, and offers on all things government benefits.


















